The wideness and complexity of “Circular Economy” topic can be a challenge towards the achievement of applicable results. In order to effectively contribute to the objective of EU Circular Economy Package, RE-CORD identified clear targets and strategic programme, focused on processing waste materials to extract specific, high value products. Thanks to its multidisciplinary expertise, RE-CORD approach to circular economy consists in the application of thermo-chemical conversion technologies to a wide range of organic feedstocks, with a focus on those waste materials which are daily produced by both urban and industrial activities.
Re-Cord scientists and engineers are daily engaged to analyse and design innovative solutions processing waste material extracting sustainable products. The waste materials (named European Waste Categories) object of Re-Cord activity on circular economy can be summarized as follows:
There is a wide range of high value products which can be derived from waste streams. The European Commission itself identifies, as a priority, to use residues as resource to produce biofuels, biofertilizers, and other 27 materials, identified as Critical Raw Materials (CRM), i.e. those raw materials which are economically and strategically important for the European economy, but have a high-risk associated with their supply and for which there is a lack of (viable) substitutes.
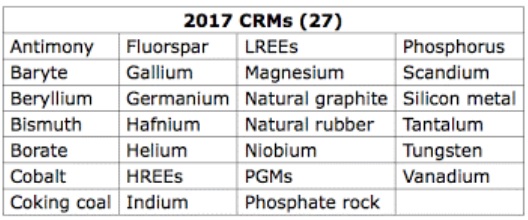
The waste categories identified above represent valuable resources useful for producing biofuels, organic fertilizers, but also some of the most important CRMs, in particular: Phosphorus, Silicon, Coking Coal, Magnesium, and Borate.
Our aim is to promote the valorisation of all above-mentioned waste materials by adopting advanced conversion processes, able to turn residual matter into bioproducts, biofertilizers and raw materials. Thanks to the multidisciplinary experience of its team, RE-CORD is able to identify the optimal procedure to effectively valorise the waste material. For this reason, RE-CORD is member of the Italian Circular Economy Stakeholders’ platform (ICESP), and of the Italian Phosphorus Platform, where we contribute to the identification of best practices, and innovative technologies. The spectrum of RE-CORD activities concerning waste recovery is the following.
Performing a complete analysis of residual stream allows the team to assess the quality of the material. The qualitative aspects are represented by:
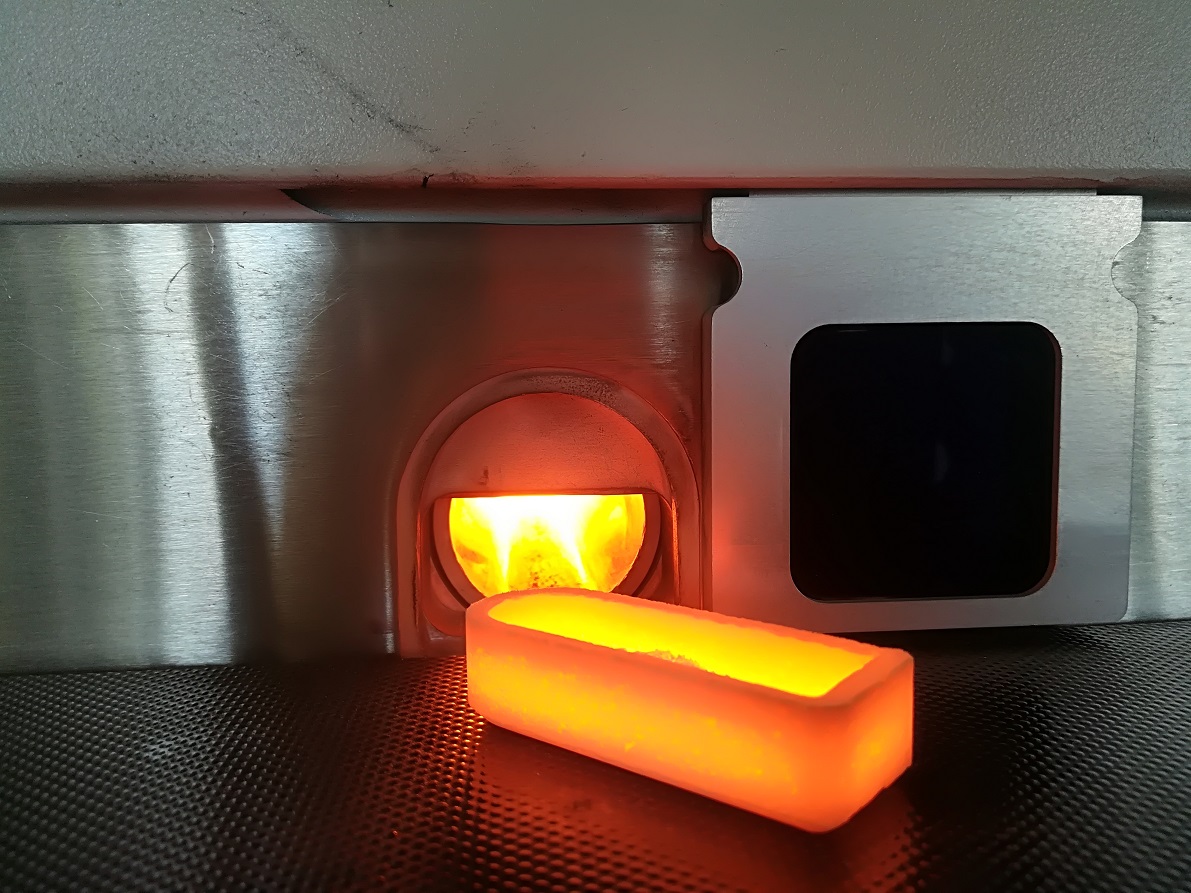

Depending on the specific type of waste material, RE-CORD can perform a broad range of test in its experimental area.
RE-CORD has a scientific approach to the theme of circular economy and its team is continuously working to improve and develop technologies able to process specific streams with high performances. For this reason, the consortium’s activity involves the design of new components and innovative machineries able to optimize the underlying thermo-chemical processes and thus effectively turning waste into reliable, sustainable products.